Triceps tendonitis is inflammation of the triceps tendon, which connects the triceps muscle at the back of the upper arm to the elbow. This condition can cause significant discomfort and hinder daily activities, especially for those who rely on their arm strength. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options available is essential for anyone experiencing muscle pain in this area.
What Is Triceps Tendonitis?
Triceps tendonitis is inflammation of the triceps tendon. It is often due to repetitive strain or overuse. The triceps muscle, which plays a crucial role in extending the arm, can sustain microtears during physical activities. While microtears are common and typically heal with rest, excessive strain can lead to larger tears that result in muscle pain and functional limitations.
Anatomy of the Triceps
The triceps muscle consists of three parts: the long, lateral, and medial heads. Each head starts at a different point—either just below the shoulder blade or along the upper arm bone—and all come together at the elbow. This unique structure allows the triceps to control movements like pushing and lifting.
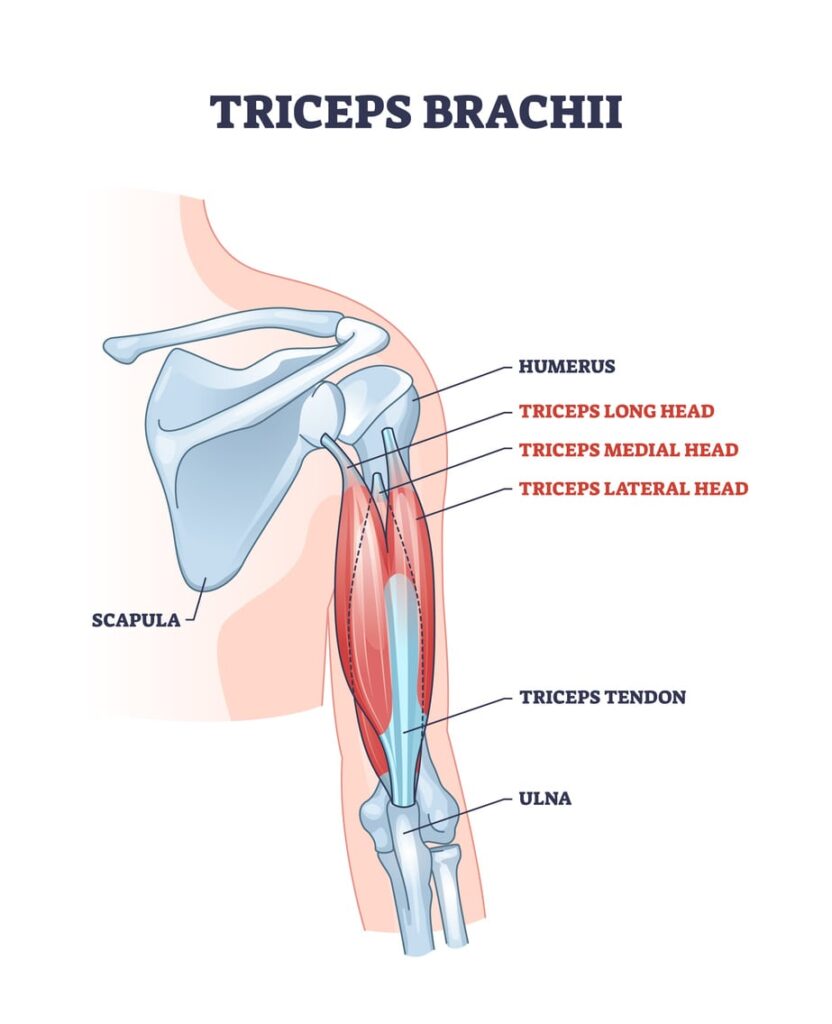
Tendons, which are strong and flexible tissues, connect muscles to bones and are key to movement and stability. Specifically, the triceps tendon links the triceps muscle to the elbow joint, enabling smooth arm extension. If this tendon becomes inflamed, it can cause muscle pain and make movement difficult.
Symptoms of Triceps Tendonitis
Those suffering from triceps tendonitis may experience a variety of symptoms that can range from mild to severe. Recognizing these symptoms early can help in seeking the proper treatment. Common symptoms include:
- Pain in the Elbow: Pain is often felt at the back of the elbow and may worsen with activities that involve arm extension, such as pushing or lifting.
- Swelling and Tenderness: The area around the triceps tendon may appear swollen and tender to the touch.
- Grating Sensation: When moving the elbow, a grating or grinding feeling may occur, indicating irritation in the tendon.
- Redness or Warmth: Inflammation can cause the skin over the tendon to become red or warm to the touch.
- Decreased Range of Motion: Individuals may find it challenging to fully extend or flex the arm without discomfort.
The severity of symptoms can vary widely. Mild cases may resolve with simple rest and home remedies, while more severe cases may require medical intervention.
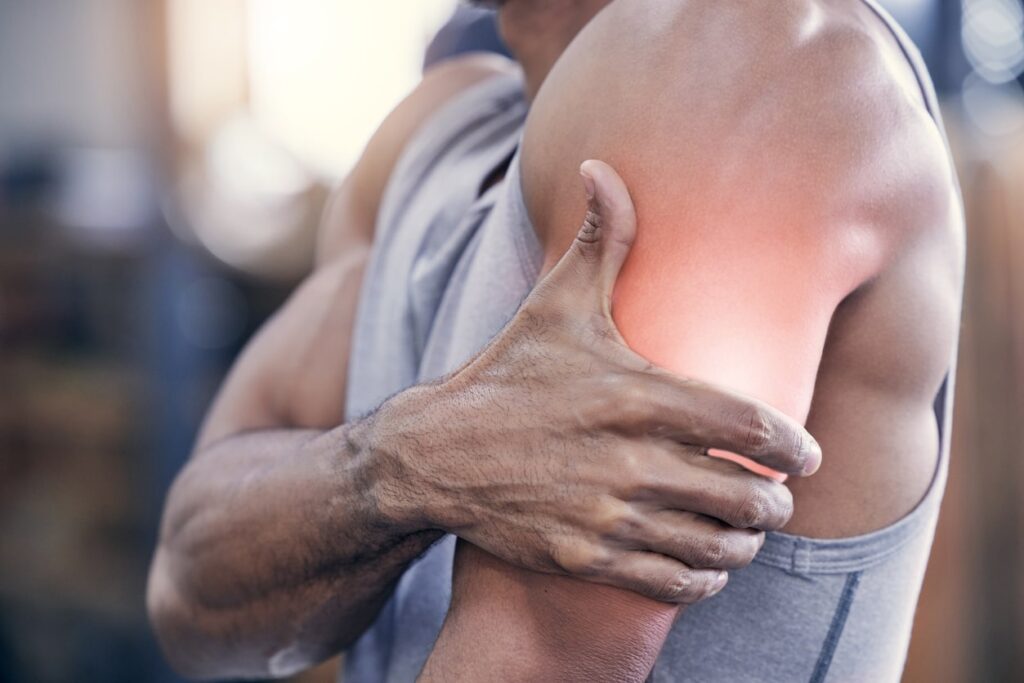
Causes of Triceps Tendonitis
Understanding the underlying causes of triceps tendonitis can help in prevention and management. The condition is often linked to specific activities and lifestyle factors. Common causes include:
- Overuse: Repetitive movements, such as weightlifting or certain sports, can lead to overuse injuries. Athletes are at higher risk, especially those involved in throwing or pushing movements.
- Poor Technique: Engaging in physical activities with improper form can place undue stress on the triceps tendon, increasing the likelihood of injury.
- Sudden Increases in Activity: Jumping into a new exercise routine or significantly increasing intensity without adequate conditioning can lead to tendonitis.
- Age-Related Changes: As individuals age, tendons become less flexible and more susceptible to injury, making older adults more prone to tendonitis.
- Underlying Medical Conditions: Certain health issues, such as diabetes or autoimmune disorders like rheumatoid arthritis, can contribute to the development of tendonitis.
Diagnosis of Triceps Tendonitis
If you suspect you have triceps tendonitis, Dr. Peter Howard will perform a thorough evaluation to confirm the diagnosis. This process may involve several steps, such as:
- Physical Examination: Dr. Howard will assess the affected area, checking for tenderness, swelling, and range of motion.
- Medical History: A detailed history of your symptoms will be taken, including when they started and any activities that may have contributed to the condition.
- Imaging Tests: If necessary, imaging studies such as X-rays, ultrasounds, or MRIs may be ordered to visualize the tendon and rule out other injuries.
Treatment Options for Triceps Tendonitis
The treatment approach for triceps tendonitis often depends on the severity of the condition. A combination of rest, physical therapy, and, in some cases, medical intervention can provide relief.
Conservative Treatment Strategies:
- Rest and Activity Modification: Taking a break from activities that exacerbate the pain is crucial. Once symptoms improve, you can gradually return to normal activities.
- Ice Therapy: Applying ice to the affected area can help reduce inflammation and alleviate muscle pain. Do this 20 minutes at a time, several times a day.
- Compression and Elevation: A compression bandage can support and reduce swelling. Keeping the arm elevated above heart level can also help decrease inflammation.
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relief: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen or naproxen, can help manage muscle pain and inflammation.
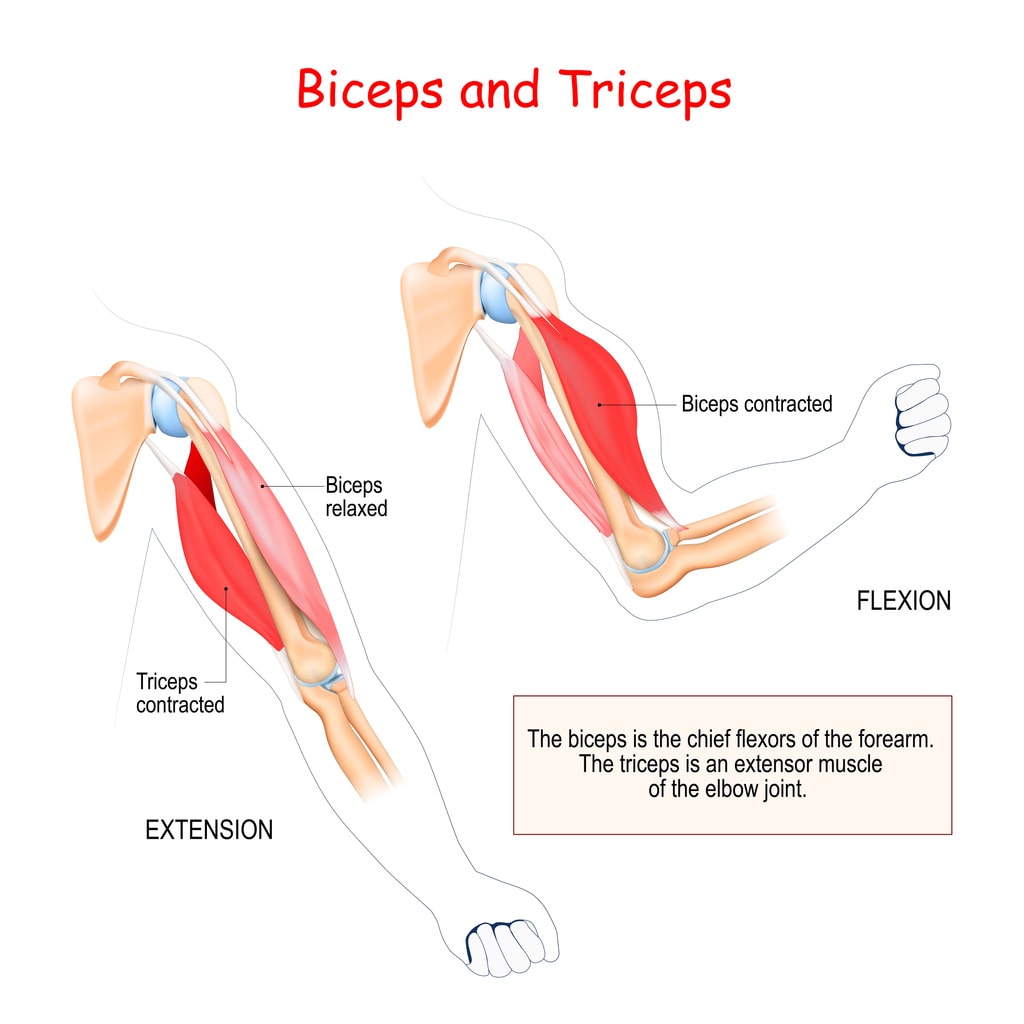
Physical Therapy
Engaging in physical therapy can be particularly beneficial for those with triceps tendonitis. A physical therapist can design a tailored exercise program that focuses on:
- Strengthening: Gradually strengthening the triceps and surrounding muscles can improve stability and reduce the risk of future injuries.
- Stretching: Incorporating stretching exercises can enhance flexibility and promote a better range of motion.
- Technique Improvement: Proper exercise techniques can help prevent re-injury and promote safe movement patterns.
Surgical Options
In cases where conservative treatments fail to provide relief, surgical intervention may be necessary. Surgical options can include:
- Tendon Repair: This procedure involves reattaching the damaged tendon to the elbow bone.
- Tendon Grafting: If the tendon is severely damaged, a graft may be used to replace the injured tissue.
Prevention of Triceps Tendonitis
To prevent triceps tendonitis, warm up before each workout. This will increase blood flow to your muscles. Ensure you use correct exercise techniques to lower your risk of injury and build up workout intensity slowly to give your body time to adjust. Pay attention to muscle pain—if it lasts, take a break and consider seeing a doctor. Some home care can help with mild triceps tendonitis. Rest the area for a few days, and apply ice for 20 minutes at a time, several times daily, to reduce swelling. Try gentle stretching to keep your arm flexible when the muscle pain decreases. Wearing a brace can also help support your arm while it is healing.
Contact Us for Care
Don’t let triceps tendonitis hold you back. You can get back to your regular activities pain-free with the proper treatment. Whether you need conservative care, physical therapy, or surgery, Dr. Peter Howard is here to help. Prioritize your health—reach out today for the treatment and support you need.
