Tibial and femoral osteotomy are surgeries that help fix misalignment in the knee, often caused by conditions like osteoarthritis or injuries. These procedures involve realigning the tibia (shinbone) or femur (thighbone) to improve the knee’s function, reduce pain, and prevent further damage. By shifting weight away from the worn-out part of the knee, these surgeries can help patients stay active and avoid more serious procedures, like a knee replacement. If you’re struggling with knee pain or limited movement, tibial and femoral osteotomy may be a good option to consider.
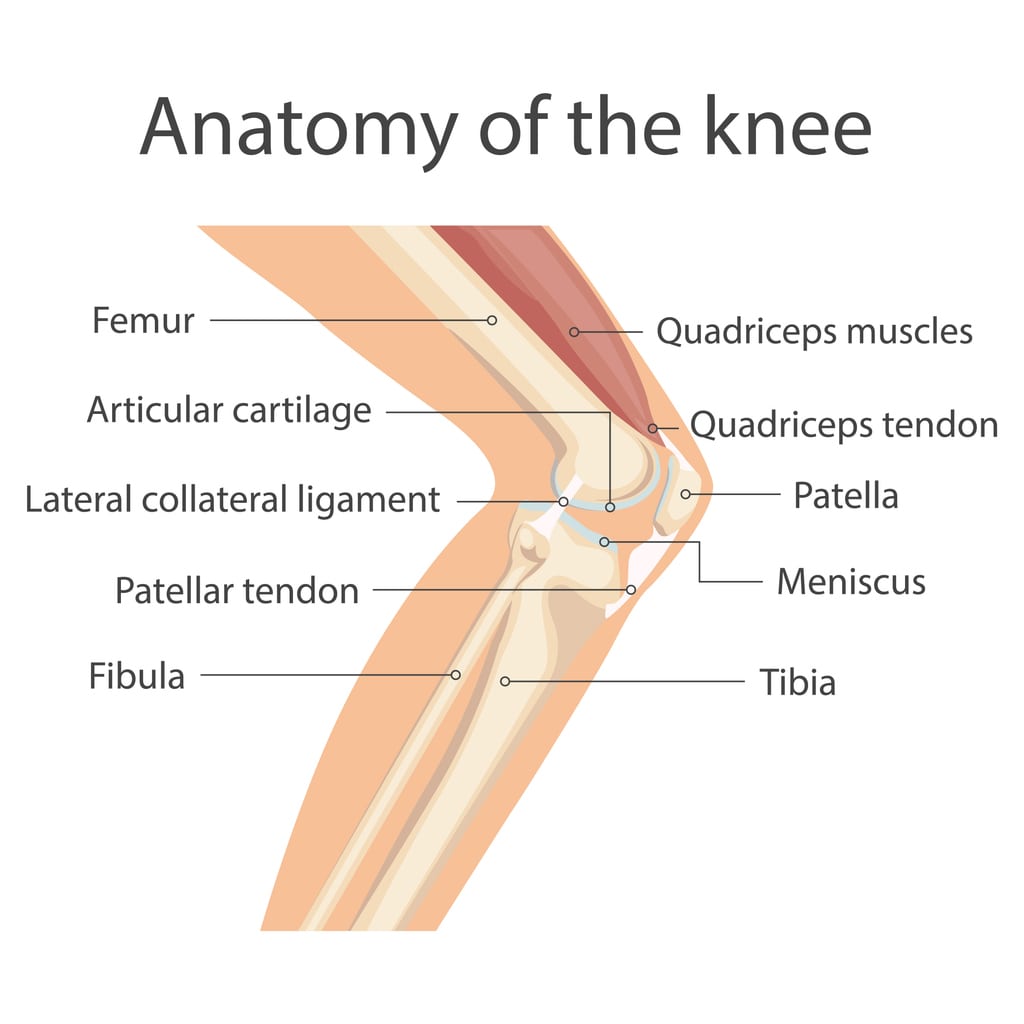
What Are Osteotomies?
Osteotomies are surgeries that cut and reposition bones to fix alignment problems. When the bones in the knee aren’t properly aligned, it can cause uneven wear on the joint, leading to pain and limited movement. These surgeries aim to realign the bones, helping to spread weight more evenly and reduce pressure on the damaged areas. The knee is a complex joint made up of the femur (thighbone), tibia (shinbone), and patella (kneecap), and all these parts need to work together smoothly. Misalignment can lead to conditions like:
- Genu Varum (Bow Legs): This occurs when the knees curve outward, placing undue stress on the inner compartment of the knee.
- Genu Valgum (Knock Knees): This is when the knees touch, but the feet are apart. It puts excess pressure on the outer knee.
Types of Osteotomies
There are primarily two types of osteotomies performed on the knee. Each serves a specific purpose based on the location and nature of the malalignment.
- Femoral Osteotomy: This surgery targets the thighbone (femur). It often pairs with tibial osteotomy to correct alignment.
- Tibial Osteotomy: A tibial osteotomy focuses on the shinbone (tibia). It is often indicated for patients with unicompartmental osteoarthritis. This is especially true when the inner compartment of the knee is affected.
Indications for Osteotomy
Knowing when an osteotomy is needed can help patients choose their treatments. Common indicators include:
- Unicompartmental Osteoarthritis: If only one compartment of the knee is affected, osteotomy can help delay or avoid total knee replacement.
- Malalignment Syndromes: Conditions like genu varum or valgum may need surgery to correct the alignment and prevent joint damage.
- Meniscal Damage: If a meniscus tear occurs with malalignment, an osteotomy may help. It can aid healing and restore function.
- Post-Traumatic Arthritis: After a serious knee injury, like a fracture or ligament tear, osteotomy can fix any misalignment. This can reduce the risk of further joint degeneration.
- Leg Length Discrepancy: If one leg is shorter due to a congenital condition or injury, osteotomy can help. It can correct the discrepancy and improve joint function and alignment.
Diagnosis
To determine if an osteotomy is needed, your doctor will start by reviewing your medical history and conducting a physical exam. They will look for signs of pain, stiffness, or limited movement and ask about any past injuries or conditions that may have caused misalignment. Imaging tests like X-rays or MRIs will help assess joint damage and alignment, and a CT scan may be used for more detailed information.
Based on these findings, the surgeon will decide if an osteotomy is the right treatment. They will consider factors like the severity of the misalignment, your age, activity level, and overall health. The goal is to improve joint function, reduce pain, and prevent further damage.

Tibial Osteotomy Procedure and Recovery
A tibial osteotomy is a surgery that involves making a small incision in the shin bone (tibia) to realign it and relieve pressure on the knee joint. This procedure is usually done under general anesthesia. Depending on the severity of the knee issue, the surgeon may use a closed or open method. The surgeon cuts and repositions the tibia to fix any misalignment, often caused by osteoarthritis or other conditions. To keep the bone in place while it heals, they may use metal plates or screws.
Recovery from a tibial osteotomy can take several months. Patients usually use crutches or a brace for the first few weeks. This limits movement and supports healing. Physical therapy is an important part of recovery, helping you regain strength and range of motion in your knee. Full recovery can take anywhere from 6 to 12 months, but most people experience pain relief and improved knee function. The procedure is very effective for those wanting to delay knee replacement surgery.
Femoral Osteotomy Procedure and Recovery
A femoral osteotomy is a surgery that involves cutting the thigh bone (femur) to realign it. It’s often used to correct misalignment caused by osteoarthritis or birth defects. The procedure is done under general anesthesia, and the surgeon carefully cuts and repositions the femur to relieve stress on the knee or hip joint. If needed, the surgeon will secure the bone in place with metal plates, screws, or rods.
After a femoral osteotomy, recovery involves limited weight-bearing and using crutches or a walker for the first few weeks. Physical therapy is necessary to help you regain strength, mobility, and range of motion in the leg. Full recovery can take several months, with some patients experiencing complete healing in up to a year. Most people see a significant improvement in knee or hip function after the surgery.
Tips for a Successful Recovery After Osteotomy
Recovery after osteotomy requires time, patience, and careful attention to the body’s needs. Following these tips can help ensure a smoother healing process and better long-term outcomes:
- Stay Active: Gradually increase activity to boost circulation and prevent stiffness. But, avoid high-impact movements until your doctor clears you.
- Follow Post-Op Instructions: Stick to your surgeon’s guidelines on activities, medications, and follow-ups to avoid complications.
- Engage in Physical Therapy: Do the prescribed therapy. It will strengthen your muscles, improve your range of motion, and stabilize your joints.
- Manage Pain and Swelling: Use prescribed medications and ice or elevation to manage pain and reduce swelling in the affected area.
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: A balanced diet aids healing. It provides essential vitamins and minerals for bones and tissues.

Contact Us for Care
If you’re dealing with joint pain or misalignment, Dr. Peter Howard, M.D., can help you find the right treatment. Whether you’re considering a tibial or femoral osteotomy or simply need advice on joint health, Dr. Howard will guide you through your options to help you get back to a pain-free, active lifestyle.
Reach out today to schedule an appointment and start your journey toward recovery.
