Knee sepsis, or septic arthritis of the knee, is a serious and life-threatening condition. It happens when bacteria, viruses, or fungi infect the knee joint. This infection causes inflammation, pain, and swelling. It can make movement hard and lead to a lot of discomfort. Knee sepsis can get worse quickly without prompt medical help. This can lead to serious joint damage and spread the infection to other body parts. In severe cases, it can even cause life-threatening complications like sepsis. Knowing the causes, spotting early signs, and getting quick treatment are key to avoiding lasting damage.
What Is Knee Sepsis?
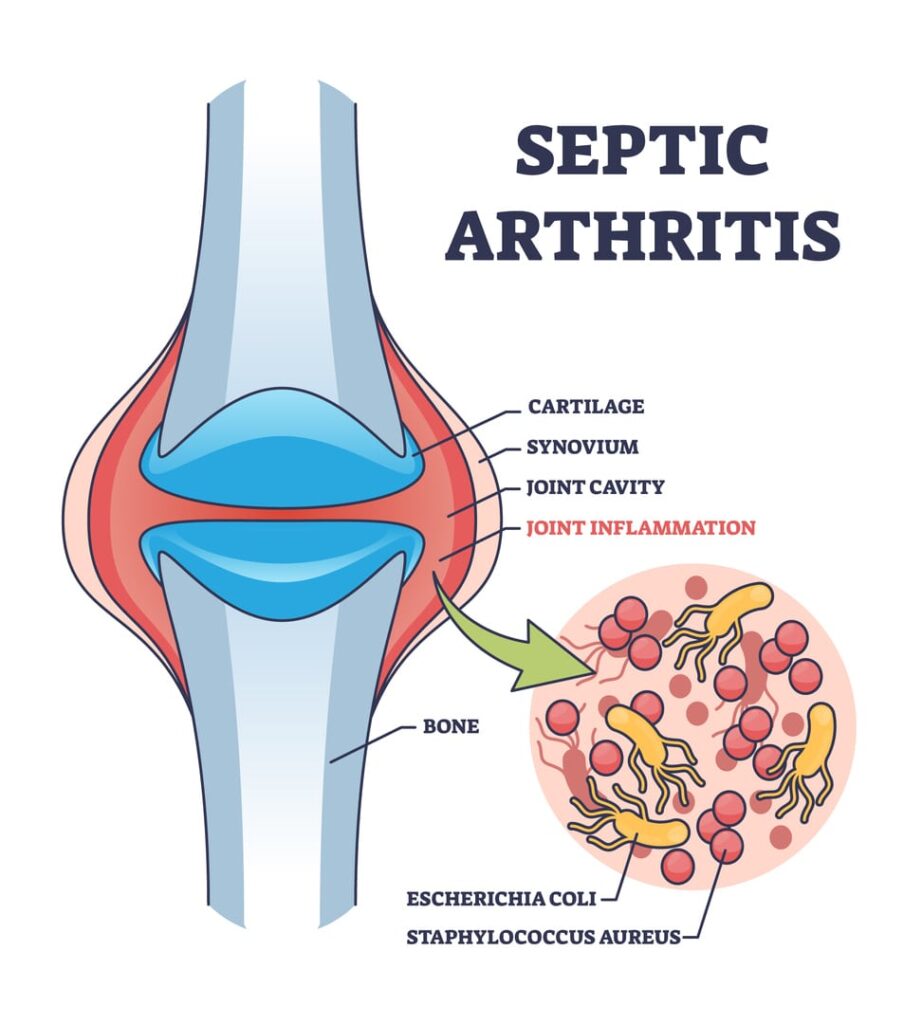
Knee sepsis is an infection that targets the knee joint, causing intense pain, swelling, and redness. This condition happens when harmful bacteria, fungi, or viruses enter the joint. This invasion often causes severe inflammation and disrupts normal joint function. Infection can come from many sources. It may start from other infections in the body, open wounds, or after knee surgery. Knee sepsis can harm the joint for a long time if not treated. In severe cases, it might cause infections in other organs. Prompt medical intervention is essential to prevent complications and protect the health of the knee joint.
Causes of Knee Sepsis
Many things can raise the risk of knee sepsis, including infections in other parts of the body, existing joint issues, and certain medical procedures. Below are some of the most common causes and risk factors associated with knee sepsis.
- Bloodstream Infections: Infections like pneumonia or urinary tract infections can spread bacteria through the bloodstream to the knee joint, causing septic arthritis.
- Direct Joint Infections: Bacteria can enter the knee through open wounds, surgeries, or injections, leading to localized infection.
- Pre-existing Joint Conditions: Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, and gout can weaken joints, making them more susceptible to infection.
- Weakened Immune System: Those with diabetes, cancer, chronic kidney disease, or currently taking immunosuppressive medications are at greater risk for infections, including knee sepsis.
- Prosthetic Knee Joints: Individuals with knee replacements face higher risks as bacteria may colonize the prosthetic joint, particularly after surgery or injury.
Symptoms of Knee Sepsis
Knee sepsis can cause a range of symptoms that can worsen quickly, signaling the need for urgent medical care. These symptoms may include:
- Intense Pain: Sharp, persistent pain in the knee, often worsening with movement or pressure, that may make walking or standing difficult.
- Swelling and Redness: The knee may appear swollen and red due to the immune response, with fluid and immune cells filling the joint.
- Warmth: The affected area feels warm or hot, indicating the body’s response to the infection.
- Fever or Chills: If the infection spreads beyond the knee joint, systemic symptoms like fever and chills may occur.
- Limited Range of Motion: Inflammation and pain can restrict movement, making it hard to fully bend or straighten the knee.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing knee sepsis involves a combination of clinical evaluation and diagnostic tests. Starting with an exam, your doctor will look for signs like redness, warmth, swelling, and limited motion. Blood tests check if your white blood cell count is high, as this can indicate there’s an infection. Imaging techniques like X-rays or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans may be used to detect any joint damage or fluid buildup in the knee.
The physician may sometimes perform joint aspiration by inserting a needle into the knee to remove fluid, which helps identify the bacteria or pathogen causing the infection. Early and accurate diagnosis is essential to prevent further complications and ensure the most effective treatment possible.
Treatment Options
Effective treatment for knee sepsis is essential to prevent long-term joint damage and serious complications. Common treatment options include:
- Antibiotics: Intravenous antibiotics are typically used to target the bacteria causing the infection, helping to control and eliminate the infection while preventing it from spreading.
- Surgical Drainage: If infected fluid accumulates in the knee, surgery may be required to drain it. This reduces pressure and inflammation and helps antibiotics work more effectively.
- Pain Management: Doctors prescribe medications such as NSAIDs or stronger pain relievers. These help manage pain and swelling, making you more comfortable while healing.
- Joint Rest and Immobilization: Resting the knee and using a brace or splint helps it heal. This prevents more damage to the joint.
- Physical Therapy: After the infection is under control, physical therapy can help. It restores strength, mobility, and flexibility, aiding the knee’s recovery and function in the long term.
Preventing Knee Sepsis
Preventing knee sepsis involves taking proactive steps to reduce the risk of infection and protect the knee joint. Here are some key preventive measures:
- Practice Proper Wound Care: Clean and cover any cuts or wounds around the knee to prevent bacteria from entering the joint. This is especially important after injuries or surgeries.
- Manage Pre-existing Joint Conditions: Keep conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, or gout under control. They can make you more prone to infections. Regular check-ups and treatment can help minimize this risk.
- Follow Post-Surgery Guidelines: After knee surgery, stick to the care instructions. Keep the surgical site clean and avoid putting extra strain on your knee.
- Boost Immune Health: Strengthen your immune system. Eat well, exercise regularly, and manage chronic conditions like diabetes and kidney disease. These conditions can increase your risk of infections.
- Care for Your Prosthetic Joint: After a knee replacement, check the joint often for infection signs. If you notice any problems, get medical help right away. Proper care and hygiene around the prosthetic are essential.
Contact Dr. Howard for Treatment
Knee sepsis is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition that requires immediate medical attention. Without prompt treatment, it can lead to severe joint damage and long-term mobility issues. If you’re experiencing pain, swelling, or difficulty moving your knee, don’t wait—seek help right away. Dr. Peter Howard specializes in orthopedic care and offers personalized treatment options to protect your knee health and restore function. Take control of your health today. Schedule a consultation with Dr. Howard to discuss your symptoms, explore treatment options, and take the first step toward a pain-free, active lifestyle. of further risk. Contact us!
