Most people don’t realize how much they rely on their hips until the simplest movements, such as standing up from a chair or rolling over in bed start to feel like a chore. That nagging ache might seem like something you can just “push through,” but when daily stiffness begins to dictate your schedule, it’s usually a sign that your body is struggling to keep up. At the office of Peter Howard, M.D., we focus on moving past surface-level symptoms to address the structural health of your hip and get you back to moving without hesitation.
Often, this persistent discomfort is the result of hip tendonitis. This common overuse injury occurs when the tendons connecting your muscles to your bones become irritated, inflamed, or begin to break down from repetitive stress. While athletes are frequently affected, everyday activities like walking, climbing stairs, or even prolonged sitting can contribute to the wear and tear. Fortunately, by understanding the role these tendons play, we can utilize advanced treatments like shockwave therapy to help you recover safely.
Understanding Tendons and Their Role in Hip Health
Tendons are the strong, rope-like tissues that connect your powerful leg muscles to your hip bones. They are the “cables” that transmit force, allowing you to walk, climb stairs, and run. Unlike muscles, tendons have a very limited blood supply. This means that once a hip tendon becomes irritated from repetitive use, it struggles to repair itself. Without intervention, minor irritation can turn into a chronic state where the body simply stops trying to heal the tissue.
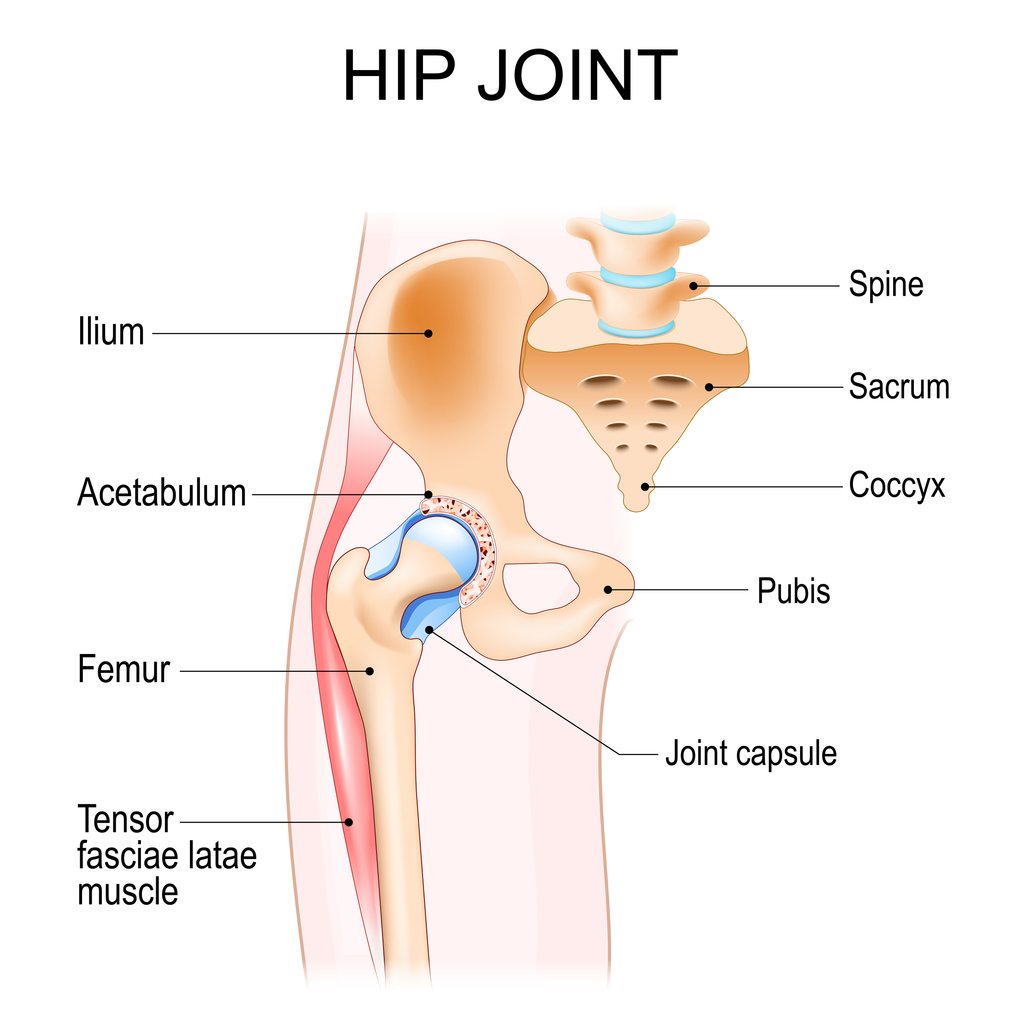
What Causes Hip Tendonitis?
Hip tendonitis occurs when the tendons experience repeated stress faster than they can repair themselves. Over time, this can lead to irritation, small tears, and tendon degeneration. Common contributors include:
- Repetitive Activities: Sports or exercises that involve running, jumping, or sudden changes in direction can overload the hip tendons, gradually weakening them.
- Sudden Increase in Activity: A rapid rise in exercise intensity or duration gives the tendon little time to adapt, increasing injury risk.
- Muscle Imbalances or Weakness: Weak glutes or tight hip flexors can place extra strain on the tendons.
- Improper Form or Biomechanics: Poor posture, abnormal gait, or incorrect lifting techniques can stress the hip tendons over time.
- Age-Related Degeneration: Tendons naturally lose elasticity and strength as we age, making them more susceptible to inflammation.
Symptoms of Hip Tendonitis
Symptoms often develop gradually and can worsen with repeated stress. Pain may start mild but can interfere with daily activities if left untreated. Common signs include:
- Hip or Groin Pain: Tenderness or sharp pain in the outer hip, groin, or buttock, often worsening with activity. This discomfort can make simple movements like walking, bending, or getting up from a chair painful.
- Stiffness: Hip stiffness, especially after sitting for long periods or first thing in the morning, which may make it difficult to move freely or perform routine activities.
- Swelling or Tenderness: Mild swelling or sensitivity over the affected tendon. You may notice the area feels firm to the touch, and pressure can increase discomfort.
- Weakness: Difficulty lifting the leg, climbing stairs, or performing athletic movements. Muscle weakness can reduce stability and make balance and everyday movements more challenging.
- Pain With Activity: Discomfort that increases during running, walking, or exercising, potentially limiting your daily activity or preventing you from participating in sports or other physical routines.
Diagnosing Hip Tendonitis
Diagnosing hip tendonitis typically involves a hands-on evaluation to identify the affected tendon, assess range of motion, strength, and posture, and review activity habits or repetitive movements that may contribute to tendon stress. Imaging tests such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or ultrasound (US) may be used to confirm the diagnosis or rule out other conditions like bursitis or labral injuries. This thorough approach allows the team at Peter Howard, M.D., to create a personalized treatment plan that reduces pain, restores function, and supports safe recovery.
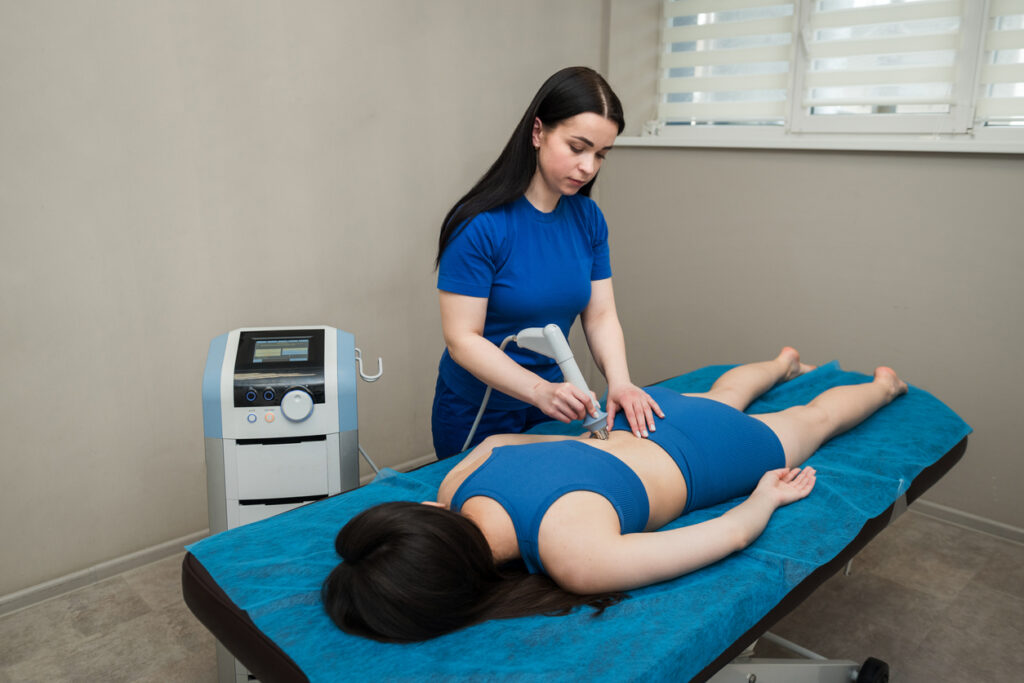
Treatment Options
Most patients improve with a structured treatment plan designed to reduce stress on the hip tendon, restore strength, and improve flexibility. Treatment often begins with activity modification, such as adjusting running, cycling, or daily movement patterns to allow the tendon to heal. Targeted stretching and strengthening exercises help rebuild tendon resilience, while physical therapy can correct imbalances, improve hip mechanics, and gradually strengthen the tendon. For persistent cases, shockwave therapy is a highly effective, noninvasive treatment that stimulates healing, reduces discomfort, and helps patients return to activity safely and comfortably.
Introducing Shockwave Therapy for Healing Hip Tendonitis
Shockwave therapy is a noninvasive treatment that delivers focused, high-energy acoustic waves directly to the injured tendon. These waves stimulate blood flow, trigger the body’s natural healing response, and encourage the regeneration of healthy tendon tissue. By breaking down damaged fibers and promoting collagen production, shockwave therapy can help in several ways:
- Improved Circulation: Enhances blood flow to support the tendon’s natural repair process.
- Tissue Remodeling: Breaks down damaged tendon fibers and encourages healthy tissue formation, improving strength and flexibility over time.
- Pain Reduction: Soothes irritated nerve endings to decrease discomfort, helping daily activities feel easier.
- Accelerated Healing Response: Encourages the tendon to repair and strengthen more effectively, potentially shortening recovery time.
- Noninvasive Relief: Offers an alternative to injections or surgery with minimal downtime. Patients typically return to normal activities shortly after treatment.
Now offered at Peter Howard, M.D., many patients notice improvements after just a few treatments.
How Shockwave Therapy Supports Tendon Healing
Tendons have a limited blood supply, which means they often heal more slowly than other tissues and can become a source of long-term pain if not properly treated. Shockwave therapy helps address this by stimulating circulation and activating the body’s natural repair processes at the cellular level. During treatment, patients typically feel a rhythmic tapping or pulsing sensation over the affected area, which is generally well tolerated and does not require anesthesia. Sessions are brief, and most people can return to normal activities shortly afterward. This makes shockwave therapy an appealing option for individuals with persistent tendon pain who want to avoid injections or surgery while still promoting meaningful, long-term healing.
When to Seek Care
If your hip pain persists for more than a few weeks, worsens with activity, or interferes with walking, climbing stairs, or exercising, it’s important to seek an evaluation. Ignoring ongoing tendon pain can lead to further tissue damage, reduced mobility, and longer recovery times. Early assessment can help identify the source of your symptoms, prevent the condition from becoming chronic, and allow you to return to your normal activities more safely and comfortably.
Contact Us
If you’re experiencing hip tendonitis symptoms or are curious whether shockwave therapy could be right for you, our team at Peter Howard, M.D. is here to help. We provide thorough, personalized care to evaluate your tendon, identify contributing factors, and recommend the most effective treatment plan for your needs. From activity modification and physical therapy to advanced options like shockwave therapy, we work with you to restore strength, flexibility, and function. Contact us today to schedule an appointment and take the first step toward a more comfortable, active lifestyle.