Endoscopic hip abductor repair is a minimally invasive surgery that treats tears or injuries to the hip abductor tendons, which help stabilize the hip and allow movement. This method uses small cuts and special tools to help surgeons fix damaged tendons while causing less harm to nearby tissues. As a result, patients experience shorter recovery times, reduced scarring, and less pain compared to traditional open surgery. This procedure helps restore mobility and improve life quality for people with hip abductor injuries.
What Is Endoscopic Hip Abductor Repair?
Endoscopic hip abductor repair treats injuries to the hip abductor. This includes tendon tears and tendinopathy, which are degenerative changes in the tendons. The procedure uses an endoscope, a small camera that helps the surgeon see the affected area inside the hip joint. This technique has many benefits compared to open surgery. It uses smaller cuts, lowers the chance of complications, and helps patients recover faster.
During the procedure, the surgeon repairs or reattaches the damaged tendon(s) to the bone or restores the integrity of the hip abductor muscles. The surgery can help with problems like tendonitis, tendon tears, or hip abductor degeneration. These issues are important for stability during weight-bearing activities.
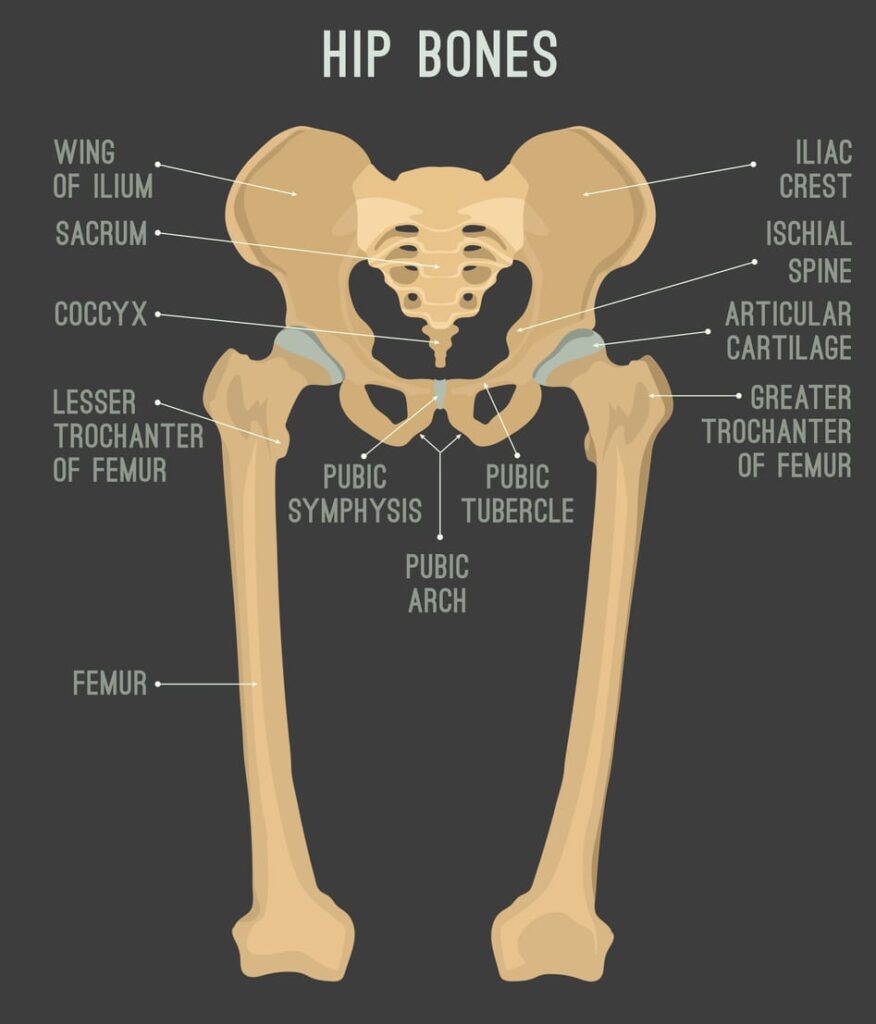
Causes of Hip Abductor Injuries
Hip abductor injuries can develop due to a combination of factors that place stress on the muscles and tendons surrounding the hip joint. Common causes include the following:
- Overuse or Repetitive Stress: Athletes or individuals who engage in activities involving repetitive movements such as running, cycling, or jumping are prone to hip abductor injuries. The constant demand placed on the hip abductors can lead to tendonitis or small tears in the tendons.
- Acute Trauma or Injury: Direct trauma to the hip or a fall can cause damage to the hip abductor tendons. This is more common in contact sports or high-impact activities.
- Age-Related Degeneration: As individuals age, the tendons of the hip abductors may undergo degenerative changes. This can weaken the tendons, making them more susceptible to tears or injuries with minimal exertion.
- Hip Impingement or Structural Abnormalities: Issues in the hip joint, like femoroacetabular impingement (FAI), can cause abnormal pressure on the hip abductors. This pressure may lead to tendon irritation or tears.
- Poor Biomechanics: When walking patterns are off or alignment is poor, the hip abductors are put under extra strain, which can cause chronic injuries over time.
Symptoms of Hip Abductor Injury
People with hip abductor injuries often face symptoms that impact their movement and quality of life. Common symptoms include:
- Lateral Hip Pain: This pain occurs on the outer hip. It often gets worse with activities like walking, running, or standing for a long time.
- Weakness or Instability: Trouble with activities needing balance, like walking upstairs or standing on one leg, because of weak hip abductors.
- Pain with Resistance: More pain occurs during movements that use the hip abductors, like leg lifts or side-lying exercises.
- Swelling and Tenderness: Swelling in the hip region and tenderness along the hip’s outer side.
- Limited Range of Motion: Trouble with moving the leg away from the body or rotating it outward.
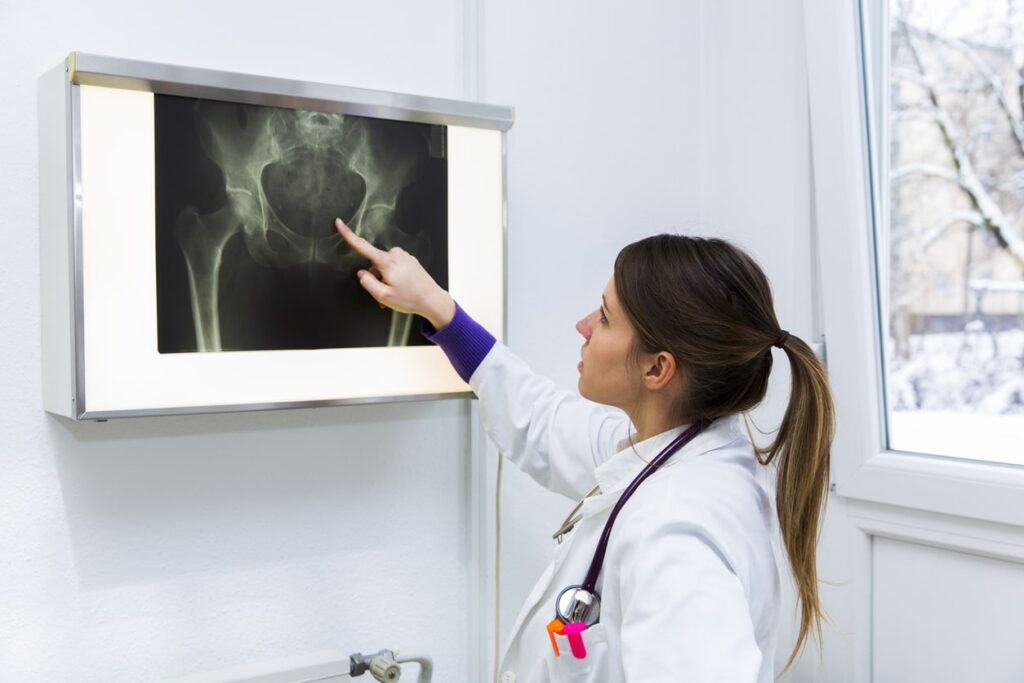
Diagnosis
Diagnosing hip abductor injuries involves a thorough evaluation of symptoms, physical
examination, and imaging tests. Dr. Howard will start by checking the patient’s medical history. Then, he will talk about any hip pain, weakness, or instability. During the physical exam, the doctor may do movement tests. These tests check the affected area’s strength, range of motion, and tenderness. Imaging studies can confirm the diagnosis and show how bad the injury is. These may include ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or X-rays. An MRI is great for spotting muscle or tendon tears. Ultrasound, on the other hand, helps check soft tissue damage in real time. Accurate diagnosis is essential for developing an effective treatment plan and preventing further complications.
Endoscopic Hip Abductor Repair: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
The endoscopic hip abductor repair procedure uses general or regional anesthesia, depending on the patient’s condition. It typically involves the following steps:
- Preparation and Positioning: The surgeon positions the patient on their side or stomach. This choice depends on the surgeon’s preference and where the injury is located. The affected hip is cleaned and sterilized.
- Incisions and Insertion of the Endoscope: The surgeon makes several small incisions around the hip area (usually no longer than 1-2 centimeters in length). The surgeon inserts an endoscope through a small incision. This helps them see the damaged tendon and nearby areas.
- Repair or Reconstruction: The surgeon uses special tools through small cuts to fix or reattach the torn tendon to the bone. Sometimes, the surgeon has to take out damaged tissue. They may also smooth rough spots on the bone to help the tendon heal well.
- Closure and Dressing: Once the repair is complete, the incisions are closed with sutures or staples, and a sterile dressing is applied to the area.
- Post-Operative Care: After the procedure, the patient will be monitored as the anesthesia wears off. Pain management and instructions for post-surgical care are provided.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Recovery after hip abductor repair focuses on restoring strength, stability, and function while reducing the risk of re-injury. In the early stages, protecting the repaired tissue is key, often requiring limited weight-bearing and the use of crutches or other assistive devices. As healing progresses, physical therapy plays a crucial role in improving mobility, rebuilding muscle strength, and enhancing hip stability. Stretching and strengthening exercises gradually become more intense, helping patients regain proper movement patterns. Recovery time varies based on the severity of the injury and individual healing rates. Following medical advice, avoiding overexertion, and sticking to a structured rehab plan are essential for a successful recovery.
Contact Dr. Howard for Treatment
Hip abductor injuries can impact your movement and daily life, but with the right diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation, recovery is possible. If you’re experiencing persistent hip pain, weakness, or instability, seeking expert care is crucial to prevent further complications. Dr. Peter Howard specializes in advanced orthopedic treatments and will create a personalized plan to help you regain function and return to an active lifestyle. Schedule an appointment with Dr. Howard today and take the first step toward recovery.
